Summary:
■ IPG1094 is a highly innovative, first-in-class, brain-penetrant small-molecule inhibitor of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) tautomerase activity.
■ It is the world's first selective MIF inhibitor to enter the clinical stage, positioning it as a groundbreaking therapeutic candidate with a unique dual-action potential in both immuno-oncology and neurology.
■ By precisely targeting the enzymatic activity of MIF, IPG1094 is designed to overcome critical challenges in two distinct areas of high unmet need: reversing tumor-induced immunosuppression to treat brain metastases in oncology, and reducing neuroinflammation to provide a disease-modifying therapy for acute ischemic stroke.
■ With a novel chemical structure, a favorable safety profile established in its completed Phase 1 trial, and a first-mover advantage, IPG1094 holds the potential to become a transformative therapy in multiple high-value indications.
IPG1094 in Oncology
Mechanism of Action

■ In the tumor microenvironment, many cancers secrete MIF via exosomes. This process drives the accumulation and function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), a dominant immunosuppressive population that blocks the antitumor activity of CD8+ T cells, allowing the cancer to evade the immune system.
■ IPG1094 inhibits the MIF tautomerase activity essential for this process, thereby reducing MDSC formation, restoring CD8+ T cell-mediated antitumor immunity, and directly suppressing tumor progression.
Key Differentiation
■ Targeting Brain Metastases: Its ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier is a critical feature, enabling it to address the significant challenge of brain metastases, where many existing therapies are ineffective.
■ Precision Immuno-Oncology: By selectively targeting the MIF-receptor axis on myeloid cells, IPG1094 precisely reprograms the tumor microenvironment without the risks of broad systemic immune impairment.
■ Potential for Combination Therapy: Its unique mechanism holds promise for synergistic use with other treatments, such as radiotherapy or immune checkpoint inhibitors, to improve outcomes for patients.
Current Development & Status
■ Phase 1/2a (Ongoing): A multi-center, open-label trial for patients with advanced primary or metastatic malignant brain tumors commenced in China.
■ Next Steps: Following the current trial, a pivotal Phase 2 study is planned to evaluate IPG1094 combined with whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) for NSCLC patients with brain metastases.
Clinical Studies
■ Pilot clinical studies on glioblastoma and lung cancer brain metastases indicate that IPG1094 treatment resulted in significant reduction of tumor size, marked revoking of brain edema, and profound amelioration of brain tumor-associated symptoms, including fatigue, nausea, headache, etc., associated with a dramatically prolonged progress-free survival (PFS).
■ Phase II trials in lung cancer brain metastases as the first indication are underway.
In vitro properties
■ Reverses Immune Suppression:In vitro studies confirmed IPG1094 completely blocks the formation of immunosuppressive MDSCs induced by pancreatic cancer exosomes and fully restores the proliferation of tumor-fighting CD8+ T cells.

In vivo Properties
■ Inhibits Tumor Growth:In a pancreatic cancer mouse model, IPG1094 treatment resulted in a significant and dose-dependent inhibition of tumor growth in vivo.

IPG1094 in ischemic stroke
Mechanism of Action

■ During an acute ischemic stroke, MIF is a pivotal pro-inflammatory cytokine that becomes markedly elevated. It drives the pathological cascade by promoting blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption, cerebral edema, and neuronal cell death.
■ By inhibiting MIF tautomerase activity at the apex of this inflammatory hierarchy, IPG1094 is designed to interrupt these processes, thereby preserving BBB integrity, attenuating endothelial and neuronal cell death, reducing infarct volume, and mitigating the resulting neurological deficits.
Key Differentiation
■ Disease-Modifying Neuroprotection: Unlike current therapies (thrombolysis, thrombectomy) that primarily focus on restoring blood flow, IPG1094 directly addresses the secondary neuroinflammatory damage that causes long-term disability.
■ Extending the Therapeutic Window: Its unique mechanism positions it as a potential disease-modifying therapy capable of extending protection beyond the acute reperfusion window, potentially benefiting a wider patient population.
■ Brain-Penetrant for Direct CNS Action: IPG1094's ability to cross the BBB is critical for stroke therapy, allowing it to directly modulate MIF activity within the central nervous system where the damage occurs.
Current Development & Status
■ Phase 1 (Completed): The completed Phase 1 trial in healthy subjects provides a strong safety and tolerability foundation for its development in the acute stroke patient population.
■ Phase 2 Initiation: IND applications for ischemic stroke have been approved by the FDA. A Phase 2 clinical trial is anticipated to commence to evaluate its efficacy and safety in acute ischemic stroke patients.
Clinical Studies
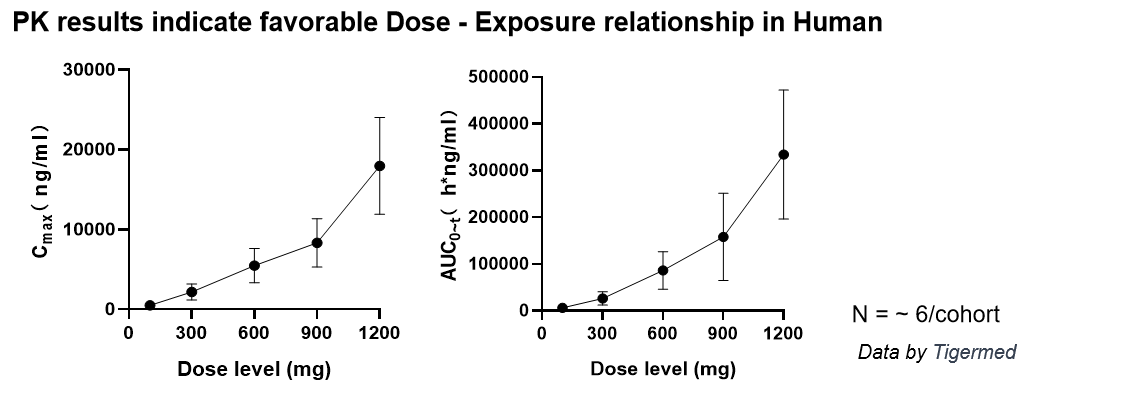
■ Phase I clinical trial indicated no severe (> grade 2) AE during dose escalation from 100 mg to 1200 mg, with linear dose-exposure relationship.
In vivo Properties
■ In a highly translatable stroke model using spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs), IPG1094 treatment significantly reduced the area of cerebral infarction.
.
■ This neuroprotective effect was accompanied by a robust and dose-dependent improvement in neurological and sensorimotor functions, including motor coordination, muscle strength, and endurance.

Publication
•Jia X, Xi J, Tian B, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Wang F, Li Z, Long J, Wang J, Fan GH, Li Q. The Tautomerase Activity of Tumor Exosomal MIF Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Progression by Modulating MDSC Differentiation. Cancer Immunol Res. 2024 Jan 3;12(1):72-90. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-23-0205. PMID: 37956411.
Cpyright © 2025 Nanjing Immunophage Biomedical Co.,Ltd
All Rights Reserved. 苏ICP备2022026466号-1  苏公网安备 32011202000830号
苏公网安备 32011202000830号
